Hello Bloggers, Welcome to Lifelong Health Blog. In this article, we come to know about The Effects of Sleep Deprivation on Your Body. When a person doesn’t get the recommended quantity of sleep, they develop sleep deprivation. Worldwide, it is estimated that sleep deprivation affects people, and its prevalence has increased recently. The term “sleep deficit” is more general. How we feel and think is directly impacted by sleep deprivation. Even one night without enough sleep can cause us to feel sleepy, irritable, and have slow thinking during the day. Sleep deprivation impairs mental function and jeopardizes physical health, though the immediate effects are more apparent. Research has connected inadequate sleep to a host of health issues, including immune system weakness and weight gain. Even though you are aware of the long-term consequences of less sleep.
If you have been playing around with your health, it’s time to stop. “Health is Wealth,” and nothing would support you if you were unable to manage and properly care for your most valuable asset—your health. Gaining knowledge about this illness’s causes, signs, diagnosis, and course of treatment can help you avoid these side effects and ensure that you get the recommended amount of sleep.
What is sleep deprivation?
Insufficient sleep causes a person to experience sleep deprivation. This could be a one-night problem that goes away, or it could be a persistent problem that lasts for weeks or even months. Lack of sleep is a common symptom of a number of illnesses, but it can also occur for a wide range of benign reasons.
Everyone needs sleep, and depending on their age, most people require a similar amount of it. The amount varies with age as well. To feel well-rested, some people do, however, require more sleep than others, though these exceptions are uncommon. Any sudden or gradual change in your sleep patterns warrants a visit with a healthcare professional.
Lack of sleep can also manifest in various ways. Some people experience sleep deprivation as a result of staying awake rather than going to sleep. Others continue to sleep, but because they’re not getting good sleep, they still feel exhausted when they wake up.
When sleep loss occurs in small, isolated doses, it typically doesn’t pose a serious issue. Nonetheless, studies indicate that a number of health problems can be brought on by or made worse by chronic sleep deprivation.
How much sleep is necessary for humans?
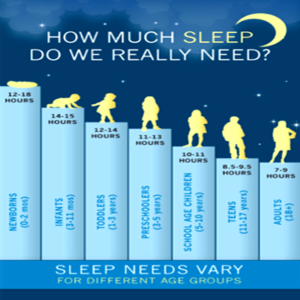
- 14 to 17 hours for newborns (up to 3 months old).
- 4 to 12 month old infants: 12 to 16 hours, naps included.
- Young children (ages 1 to 5): 10 to 14 hours, which includes naps
- Children in school (6–12 years old): 9–12 hours.
- Teens: 8 to 10 hours (ages 13 to 18).
- Adults: 7 to 9 hours (18 years and older).
How Does Getting Less Sleep Affect Your Health?
Do you get less than six to seven hours of sleep every day? Continue reading to learn the consequences of getting too little sleep. The Effects of Sleep Deprivation on Your Body are following:
Memory loss:
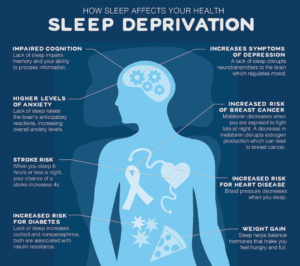
Sleep deprivation impairs memory function, both short- and long-term. Bad impact on the brain’s ability to function: Lack of sleep has a negative impact on your body and mind, impairing your ability to focus, be creative, and solve problems.
Mood swings:
The effects of sleep deprivation include unpredictable mood swings, anxiety, and in severe situations, depression.
Sleep Deprivation Ages Your Skin :
Sallow skin and puffy eyes are common after a few nights of sleep deprivation. However, it has been discovered that persistent sleep deprivation can result in dull skin, wrinkles, and dark bags under the eyes.
The stress hormone cortisol is released into your body in greater amounts when you don’t get enough sleep. Excessive levels of cortisol have the ability to degrade collagen, the protein that keeps skin elastic and smooth.
Accidents and mishaps:
One of the main consequences of insomnia is a higher chance of daytime injuries or other mishaps, including auto accidents.
Reduced immunity:
When your body doesn’t get enough sleep, it becomes less capable of defending itself against foreign invaders.
Increased risk of blood pressure:
Sleeping for less than five hours a day increases the likelihood of having high blood pressure. Because the body’s capacity to release insulin, a hormone that lowers blood sugar, is diminished, individuals who do not get enough sleep frequently have elevated blood sugar levels and are more likely to develop Type 2 Diabetes.
Pain:
Individuals who lack sleep are more likely to experience new pain or to believe that their current pain is getting worse. An unfavorable cycle of increasing pain and decreasing sleep may result from pain interfering with sleep again.
It’s Depressing to Be Sleepy :
Over time, depression symptoms may be exacerbated by sleep disorders and sleep deprivation. Individuals with a diagnosis of anxiety or depression were more likely to report getting less than six hours of sleep per night in a 2005 Sleep in America survey.
Depression is most strongly correlated with insomnia, the most prevalent sleep disorder. In a 2007 study involving 10,000 participants, depression was five times more common in those with insomnia than in those without it. Actually, sleeplessness is frequently one of the initial signs of depression.
Depression and insomnia exacerbate one another. Depression symptoms are frequently exacerbated by sleep loss, and depression itself can make it more difficult to fall asleep. Positively, treating sleep issues can aid with depression and insomnia.
Hormone levels:
Not getting enough sleep can have an impact on the synthesis of several hormones, including testosterone and growth hormones. In addition, it triggers the body to release more stress hormones like cortisol and norepinephrine.
Weight gain:
Sleep deprivation causes your body’s chemical messengers—which alert your brain when your stomach is full—to malfunction, which results in weight gain. As a result, even when you’re already full, you usually keep eating.
Kills sex drive:
Men and women who are sleep deprived report having smaller libidos and less interest in having sex, according to sleep specialists. Increased tension, tiredness, and low energy levels could be the main causes.
There might be an additional reason for the sexual slump in men who have sleep apnea, a respiratory condition that causes sleep disturbances. According to a 2002 study that was published in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism, low testosterone levels are common in men who also have sleep apnea. In the study, testosterone secretion was abnormally low at night in nearly half of the men with severe sleep apnea.
Heart diseases:
Lack of sleep can have its own set of consequences, including elevated blood pressure, elevated blood sugar, and elevated levels of chemicals associated with inflammation.
What Is the Cause of Lack of Sleep?
Occasionally, sleep deprivation has a deeper underlying cause that we might not notice right away. If you see a pattern where you are unable to make up for lost sleep, it’s critical to identify and address the potential causes of your inability to lead a healthy lifestyle. The following are a few of the most typical causes of insomnia:
Strict deadlines, night shifts, and pressure to perform well at work The majority of the time, we overpromise and accept more responsibility at work than we are truly capable of doing at the moment. Although the effects of overworking yourself might not be felt right away, it will have a negative impact on your mental and emotional health.
Chronic Mental Illnesses:
Stress, anxiety, depression, and other mental health conditions are some of the main causes that affect how well we sleep. Since they may impact many aspects of our lives, including our sleep, it is essential that we take timely action to ensure our general well-being.
Hungry:
One of the main causes of insomnia, did you know that? Our bodies require food as fuel to function, so depriving them of it interferes with their natural needs. In contrast, when we go without food, our bodies release ghrelin, which increases hunger and keeps us awake. When we eat, our bodies release the hormone leptin, which signals that our bodies are satisfied and suppresses ghrelin.
Constant Use of Electronic Devices:
Sometimes, no matter how hard we try, we just can’t seem to escape the internet, which makes it an addictive place. More often than we think, using electronics right before bed can interfere with our sleep patterns.
Treatment and Prevention of Sleep Deprivation :
There is no one solution that works for all cases of sleep deprivation because there are numerous causes. Treatment options vary depending on the underlying cause of the condition. However, there are numerous ways to treat sleep deprivation. While some treatment focuses on treating the underlying cause of sleep disruption, others aim to improve the way a person sleeps or gets ready for sleep.
Treatments for sleep deprivation and related disorders that are more frequently used include:
Deal with Lack of Sleep :
Many people accept sleep deprivation as normal, which leads to them getting insufficient sleep. Instead of making the required changes to increase their sleep, they attempt to “power through,” nap, or consume coffee or energy drinks to combat their drowsiness.
These methods don’t provide long-term fixes for sleep deprivation. They might make it through the day, but the long-term and short-term consequences of sleep deprivation will still be felt. Instead, it’s critical to prioritize getting more sleep and better-quality rest.
Make Sleep Your Top Priority :
People who sacrifice their sleep for work, play, or other responsibilities frequently suffer from chronic sleep deprivation. Prioritizing sleep is essential to preventing this. Even on weekends, you ought to make an effort to go to bed and wake up at the same times every day. When scheduling those times, remember to leave time for getting enough rest. After you’ve decided on a timetable, stick to it. Your nightly sleep should not fluctuate if your sleep schedule is stable.
Establish boundaries to ensure that you get the full amount of sleep each night, even though it can be simple for the responsibilities of your personal or professional life to eat away at your allotted time for sleep. Maintaining a consistent bedtime routine can also help you get into the proper mindset for restful sleep every night. Every night, get ready by following the same routine: brushing your teeth, putting on pajamas, and quietly reading or stretching.
Personalize Your Sleeping Space :
Create the perfect sleeping environment in your bedroom. If your bedroom is comfortable and meets your needs, you are less likely to put off going to bed. You should have plenty of support from the best mattress and pillow for your needs and preferences, and your bedding should keep you warm but not too hot. Make every effort to ensure that your bedroom is as quiet and dark as possible to reduce any potential sleep disturbances.
Steer clear of things that could disrupt your sleep :
One helpful first step in treating sleep deprivation is to steer clear of things that can interfere with your sleep, often without your knowledge. Alcohol consumption, for instance, can induce drowsiness at night but also interfere with your regular sleep pattern, lowering the consistency and quality of your sleep overall.
If you often take naps, try to limit the duration to no more than thirty minutes, and avoid taking them in the late afternoon or evening. Additionally, because caffeine can stay in your system for several hours, it is best to avoid consuming it in the late afternoon.
When you want to go to bed, you may find yourself wired because of the mental stimulation provided by TVs, computers, tablets, and smartphones. These devices’ light emissions have the potential to disrupt your circadian cycle. It is therefore advised to avoid using electronics for at least an hour before going to bed.
Drugs :
Many drugs have the ability to alter a person’s sleep patterns or help them fall asleep and stay asleep. Certain medications have the ability to alter a person’s dream patterns, reducing the likelihood of severe nightmares or other sleep disturbances. Nonetheless, medical professionals use caution when prescribing sleep aids because many of them have the potential to become habits.
Strategies for home care :
Often, it is helpful to alter sleeping patterns and the sleeping environmentTrusted Source. One is able to:
- To establish a routine, try waking up and going to bed at the same times every day—even on the weekends.
- Eat nothing two to three hours before going to bed.
- Try to sleep for twenty minutes, then get up and read before attempting to sleep again later.
- Engage in regular daytime exercise.
- Make sure the bedroom is cool, dark, and quiet.
- Electronics should be turned off and kept out of the bedroom.
- Avoid drinking too much alcohol and caffeine, especially right before bed.
- Steer clear of tobacco use.
- Apply a mouth guard to control your bruxism.
A person should see a healthcare professional if these remedies are ineffective, particularly if their quality of life is being negatively impacted by sleep deprivation.
You May Also Like : Tips for Building a Healthy Relationship
Conclusion
Sleep seems to serve a variety of vital purposes. For instance, research indicates that sleep promotes learning and memory, helps maintain mood stability, and guards against illness and infections.
The Effects of Sleep Deprivation on Your Body, The biggest error we make when trying to stay awake is reaching for coffee or energy drinks as a quick fix. For a while, this may help you focus and have more energy, but over time, it can cause sleep disruption, which can be disastrous.
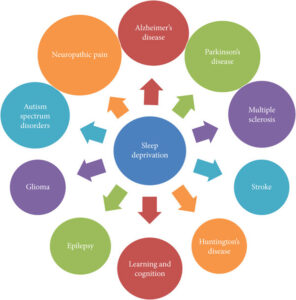
Periodically falling asleep might not be a serious problem. On the other hand, persistent lack of sleep can raise a person’s risk of developing dementia, heart disease, and diabetes, among other chronic illnesses.
To increase the quantity and quality of their sleep, a person who frequently struggles with insomnia should try some home care techniques. Anyone who has severe or ongoing sleep issues ought to consult a physician.
Frequently requested inquiries
1. What consequences does insomnia have in the long run?
Chronic sleep deprivation can negatively impact your metabolism and heart health over time. Research from Reputable Sources suggests that it might be linked to an increased risk of cancer, type 2 diabetes, and obesity.
2. Which five stages make up sleep deprivation?
The duration of the sleep deprivation cycle is referred to as the five stages. Additional adverse side effects start to appear after each stage. These are the times:
24 hours
36 hours
48 hours
72 hours
96 hours
3. When does insomnia become too severe?
The Fifth Edition of The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental DisordersAccording to a reliable source, insomnia is the inability to fall asleep or stay asleep for a minimum of three months on a regular basis.

1 thought on “The Effects of Sleep Deprivation on Your Body”